What is a Nautical Mile? – Regular Mile Vs Nautical Mile
Nautical mile refers to the distance between any two locations and is measured by traveling from one point to the other in the air or over water. Statute or regular mile on the other hand, refers to the distance between two points measured by traveling from one place to another through an imaginary straight line on the earth’s surface.
Nautical Mile
Also called International Nautical Mile, it is a unit of measurement equivalent to 1.852 kilometers or 6076 feet. It replaced the British nautical mile of 6080 feet and United States nautical mile of 6080.20, through an international agreement held in Monaco in 1929.
According to US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), “the international nautical mile of 1852 meters (6076.115 49…feet) was adopted effective July 1, 1954, for use in the United States. The value formerly used in the United States was 6080.20 feet = 1 nautical (geographical or sea) mile.”
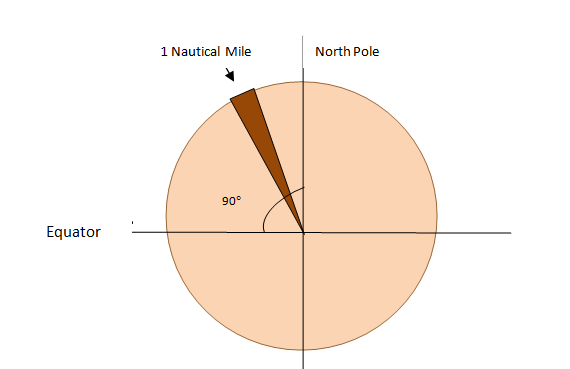
Nautical mile is based on the circumference of the earth and is used for sea or air travel. Suppose you cut the earth into half at the equator, pick half of it and look through as a circle. You then divide the circle into 360 degrees and further sub divide a degree into sixty minutes. A minute of an arc of the earth is equivalent to one nautical mile.This means that if you travel around the Earth at the equator, you would cover a total of 21,600 nautical miles (360 x 60).
A knot
The term knot dates back from the 17th Century when ancient mariners gauged the speed of their ship using a device called “common log” or chip log. In this method, knots were tied at uniform intervals in a rope which had a piece of slice shaped wood at the end. The wood was then tossed behind the ship. As the vessel moved, the rope rolled out freely for a specific time and then the number of knots were counted and used in calculating the speed of the vessel. The speed was said to be the counted number of knots.
After standardization of nautical miles in 1929, knot was agreed to be its standard unit of measuring speed, calculated based on time and distance.
Up to date, knots are used in navigation and aviation, normally shown on aircraft’s airspeed indicators and is expressed in terms of nautical miles per hour. For example, if you are moving at a speed of 1 nautical mile per hour, we say you are moving at a speed of I knot.
Nautical mile refers to the distance between any two locations in the air or over water.Click To Tweet
The Mile
The concept of mile originated from the Ancient Roman times. The Romans used to put mileposts on their roads which they used to measure distance by using a unit called mille passum, a Latin word meaning a thousand paces. Each pace was estimated to be five Roman feet, meaning one thousand paces was equivalent to 5,000 Roman feet, about 4,850 of the modern feet.
Around the year 1500 in London, mile was defined as eight furlongs. A furlong is an old English unit of length equivalent to 625 feet. During the reign of Queen Elizabeth I, 280 feet was added to the 5,000 feet of original mile, under a statute of 1593 that increased the length of a furlong to 660 feet, hence the current 5280 feet per statute mile.
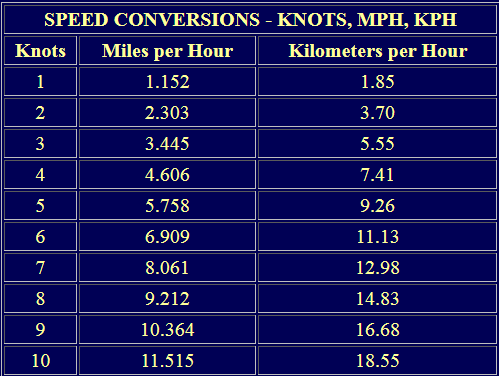
Converting Knots into Kilometers per Hour
Speed in kilometers per hour is the distance in kilometers traveled in exactly 3,600 seconds. If one kilometer is traveled in one hour, we express it as 1 km/hr.
Several calculation tools have been created to ease the work of conversion in different units.
For example, the Wind Speed Conversion Table below makes it easier to convert knots into miles or nautical miles per hour and vise versa.
1 Knot = 1 Nautical Mile per hour
1 Nautical mile = 6076.12 ft. = 1852 m
1 Statute mile = 1760 yards = 5280 feet
Why Nautical Mile is Longer than Mile
Nautical mile is measured based on the earth’s circumference and is equivalent to one minute of latitude.
A mile is based on land measurement which tends to be shorter than the circumference . The difference is brought about by the fact that Earth is not a perfect sphere but tends to be flattened at the poles.
In converting statute to nautical mile, we use factor 1.15, though it does not provide accurate results.
For Example
A statute mile = 5,280 feet
(5,280 x 1.15) =6.072 feet.
This means that the result is 4 feet shy from the actual figure of 6,076 feet of nautical mile .
Prearranged tables and converters like Bowditch’s Table 20 can be used to give more precise results.
Nautical Charts
Since nautical miles follow lines of longitude, they are very useful in navigation. Sailors and aviators have since come up with nautical charts that serves as graphical representation of the Earth and focuses on the areas of water.
These chart uses one of three map projections: polyconic, gnomyc and Mercator. Nautical charts make navigation easier in open waters making it a very important tool in shipping and exploration.
They may be in either printed or electronic navigational form. Technological advancements have made paper charts readily available, and can be printed “on demand” . This has made the work of sailors and mariners easy since they will be up to date with the most accurate information necessary for their travel.
Conclusion
Both statute and nautical miles are units of distance but are derived and used differently.
A mile is a unit of length on land that is equivalent to 5,280 feet and is part of United States standard units of measure. When compared with metric system, a mile is roughly 1,609 meters and it is abbreviated as m
A nautical mile is distance unit used for both sea and air travel and is equal to 1.151 miles or 1,852 meters. It is based on a minute of arc on the Earth’s sphere, with 3600 seconds of arc per degree longitude. It is abbreviated as nm.
Whenever you are using geographical charts, you should be sure of the distance measurement being used. This is because different charts use different measurements. Four measures commonly used on charts include:
- Nautical miles – used in ocean and coastal waters.
- Yards – used for defining distances not more than a mile.
- Meters – are units mostly used on United States and Canada charts.
- Statute miles – used for measuring distance in inland areas.